rfid tag dimensions Learn about the physical dimensions of RFID labels, the factors to consider when selecting an RFID label, including size, shape, communication range, material and environmental . The six games on the Wild Card slate will be played over a three-day span this weekend, starting with two AFC contests on Saturday and concluding with an NFC showdown on Monday night. .
0 · types of rfid labels
1 · smallest rfid tags
2 · rfid types and ranges
3 · rfid tags types
4 · rfid tag details
5 · rfid tag circuit diagram
6 · rfid cost per tag
7 · disposable rfid tags
Cybersecurity - How to steal a credit card: Loyola University Chicago: Features. “Most people are taught to be good and kind but there are people who are not, so to protect yourself you have to put yourself into their mind set.”. — Eric Chan .

types of rfid labels
In this article, we will explore the different types of RFID tags and their dimensions, providing insight into their features, applications, and considerations for implementation. Regular Tag DimensionsLearn about the physical dimensions of RFID labels, the factors to consider when selecting an RFID label, including size, shape, communication range, material and environmental .Learn about the physical dimensions of RFID labels, the factors to consider when selecting an RFID label, including size, shape, communication range, material and environmental considerations, and cost. In this article, we will explore the different types of RFID tags and their dimensions, providing insight into their features, applications, and considerations for implementation. Regular Tag Dimensions
Size and shape: Make sure the label fits your products. The size and shape of the RFID tag also influences its performance. Tags can be tiny for small products or robust for large assets. A good practice is to work with a supplier like Dipole RFID, who can customise the shape and size of the tag to your needs.RFID tag range refers to the maximum distance at which an RFID reader can effectively read the tag’s information. This range is influenced by several factors, including the type of tag, the power of the reader, and environmental conditions.Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The tag captures this energy and powers its internal chip, enabling it to transmit data back to the reader.
Not only frequency ranges, but the RFID tags also come in different sizes, shapes, dimensions to acquire the form of paper, objects, buttons, keys and much more. Antenna, microchip and battery are the essential elements of these RFID tags.Electronic component manufacturer Murata Manufacturing Co. produces the world’s smallest high-frequency (HF) tag to date. The tag measures 3.2 millimeters (0.13 inch) in width and length and 0.7 millimeter (0.03 inch) in thickness—about one-tenth the size of most other HF tags. Minimum Width: 0.50” – 0.98”. Maximum Width: 4.09” – 4.65”. Minimum Length: 0.25” – 0.35”. Maximum Length: 39” – 98”. Two other important factors to consider when printing RFID labels of different sizes are the core size and outer diameter.The smallest RFID tag on the market can be as small as a few millimeters or even smaller, such as an RFID particle tag, which is only 0.4 mm × 0.4 mm in size. These miniature RFID tags are not only small in size but also powerful, capable of accurate tracking and identification of more complex and tiny objects.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) allows devices to share information without physical contact. This technology has many uses - let's jump in and learn what it is, how it works and how you can use it. Get a quick overview and see how Rob uses the RFID Qwiic Kit to keep track of his family's M&M consumption.Learn about the physical dimensions of RFID labels, the factors to consider when selecting an RFID label, including size, shape, communication range, material and environmental considerations, and cost. In this article, we will explore the different types of RFID tags and their dimensions, providing insight into their features, applications, and considerations for implementation. Regular Tag Dimensions
Size and shape: Make sure the label fits your products. The size and shape of the RFID tag also influences its performance. Tags can be tiny for small products or robust for large assets. A good practice is to work with a supplier like Dipole RFID, who can customise the shape and size of the tag to your needs.RFID tag range refers to the maximum distance at which an RFID reader can effectively read the tag’s information. This range is influenced by several factors, including the type of tag, the power of the reader, and environmental conditions.
Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The tag captures this energy and powers its internal chip, enabling it to transmit data back to the reader.
Not only frequency ranges, but the RFID tags also come in different sizes, shapes, dimensions to acquire the form of paper, objects, buttons, keys and much more. Antenna, microchip and battery are the essential elements of these RFID tags.
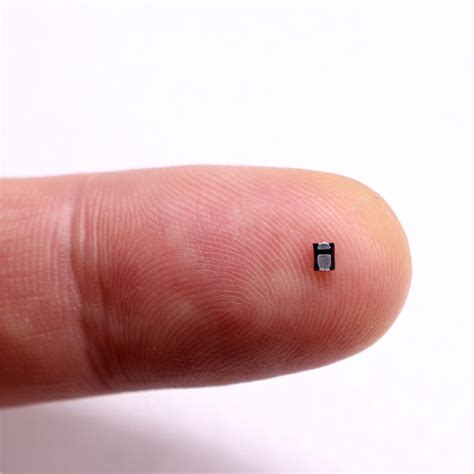
Electronic component manufacturer Murata Manufacturing Co. produces the world’s smallest high-frequency (HF) tag to date. The tag measures 3.2 millimeters (0.13 inch) in width and length and 0.7 millimeter (0.03 inch) in thickness—about one-tenth the size of most other HF tags.
Minimum Width: 0.50” – 0.98”. Maximum Width: 4.09” – 4.65”. Minimum Length: 0.25” – 0.35”. Maximum Length: 39” – 98”. Two other important factors to consider when printing RFID labels of different sizes are the core size and outer diameter.The smallest RFID tag on the market can be as small as a few millimeters or even smaller, such as an RFID particle tag, which is only 0.4 mm × 0.4 mm in size. These miniature RFID tags are not only small in size but also powerful, capable of accurate tracking and identification of more complex and tiny objects.
smallest rfid tags

keyme rfid sticker size
Unlike older generations of banking cards with magnetic stripes, EMV cards use a smart microprocessor chip technology which: 1. Secures the cardholder's credentials 2. Performs cryptographic computation to protect its communication with the Point-of-Sale . See more
rfid tag dimensions|rfid tags types