nfc frequency band NFC operates in a frequency range centered on 13.56 MHz and offers a data transmission rate . I use a MIFARE Classic NFC access card. Is there any way to clone my card on an Android device (e.g. on Samsung Galaxy Nexus or Asus Nexus 7)? Note: this question is .Make sure your phone has NFC Support, Download NFC Tools from Play Store, Open the app .
0 · what is nfc chip
1 · what is nfc capability
2 · what frequency does nfc use
3 · what does nfc stand for
4 · nfc meaning in computer
5 · nfc how does it work
6 · nfc explanation
7 · nfc capabilities
Airtel Payments Bank NCMC Enabled Cards are rechargeable card valid for multiple modes of public transport across India such as in metro, buses, ferry, etc. NCMC Enabled Card is a .
rfid reader computer definition
what is nfc chip
NFC operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, a part of the high-frequency (HF) radio spectrum, . NFC or Near Field Communications is a short-range wireless connectivity .NFC operates in a frequency range centered on 13.56 MHz and offers a data transmission rate .
what is nfc capability
NFC communicating in one or both directions uses a frequency of 13.56 MHz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band, compliant with the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 848 kbit/s.
NFC operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, a part of the high-frequency (HF) radio spectrum, and allows for both one-way and two-way communication between devices. However, its short range makes it ideal for secure, low-power exchanges. NFC or Near Field Communications is a short-range wireless connectivity technology that allows two compatible devices to communicate without contact. This two-way wireless communication technology uses radio waves operating at a .
NFC operates within the globally available and unlicensed radio frequency ISM band of 13.56 MHz and can go up to a maximum data rate of 424Kb/s, whereas Bluetooth operates in the 2.4GHz.NFC operates in a frequency range centered on 13.56 MHz and offers a data transmission rate of up to 424 kbit/s within a distance of approximately 10 centimeters.
Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 cm (11⁄2 in) or less.Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless communication technology that has revolutionized how devices interact in various industries, from payments to data sharing. This NFC tutorial guide covers protocol stack, working principles, frame structure and different communication modes.The 13.56 MHz frequency is globally accepted and standardized for NFC applications. This frequency band is a part of the high-frequency (HF) band of the radio spectrum and allows for a moderate data transfer rate and a small range of communication. RFID: RFID can operate across a wide range of frequencies, including low frequency (125 kHz), high frequency (13.56 MHz), and ultra-high frequency (865-960 MHz). The choice of frequency band impacts the range, speed, and penetration of the signal. NFC: NFC operates exclusively in the high frequency (HF) band at 13.56 MHz. This standardization .
NFC, as known as Near Field Communication, is a subset of RFID as it exploits HF (High frequency) band of RFID spectrum to transmit the data over a short-range or distance. The operating frequency of NFC is 13.56 MHz along with the two international standards named ISO/IEC 14443 and ISO/IEC 18000-3.NFC communicating in one or both directions uses a frequency of 13.56 MHz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band, compliant with the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 848 kbit/s.NFC operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, a part of the high-frequency (HF) radio spectrum, and allows for both one-way and two-way communication between devices. However, its short range makes it ideal for secure, low-power exchanges. NFC or Near Field Communications is a short-range wireless connectivity technology that allows two compatible devices to communicate without contact. This two-way wireless communication technology uses radio waves operating at a .
NFC operates within the globally available and unlicensed radio frequency ISM band of 13.56 MHz and can go up to a maximum data rate of 424Kb/s, whereas Bluetooth operates in the 2.4GHz.NFC operates in a frequency range centered on 13.56 MHz and offers a data transmission rate of up to 424 kbit/s within a distance of approximately 10 centimeters. Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 cm (11⁄2 in) or less.Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless communication technology that has revolutionized how devices interact in various industries, from payments to data sharing. This NFC tutorial guide covers protocol stack, working principles, frame structure and different communication modes.
The 13.56 MHz frequency is globally accepted and standardized for NFC applications. This frequency band is a part of the high-frequency (HF) band of the radio spectrum and allows for a moderate data transfer rate and a small range of communication.
RFID: RFID can operate across a wide range of frequencies, including low frequency (125 kHz), high frequency (13.56 MHz), and ultra-high frequency (865-960 MHz). The choice of frequency band impacts the range, speed, and penetration of the signal. NFC: NFC operates exclusively in the high frequency (HF) band at 13.56 MHz. This standardization .
what frequency does nfc use
what does nfc stand for
rfid reader and writer gipo pin
rfid reader b type
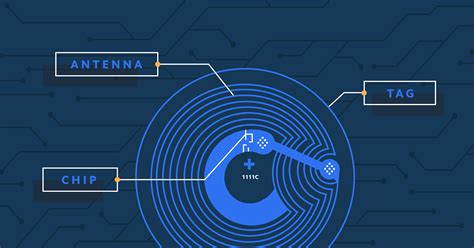
Normally it's not worth guessing, there are 2 32 (or 4 bytes) options (00 00 00 00 - FF FF FF FF) if it's a MiFare ultralight tag which are starting to get more and more common (and cheap). My app on the App Store (Smart NFC) recently added .
nfc frequency band|what does nfc stand for