rfid chip in dog A: The microchip itself is a passive RFID, which means that it uses radio waves to transmit the information it contains — in this case, your dog’s ID number and the registry’s phone number. These particular chips get powered by the radio wave energy given off by an RFID scanner, which then allows them to relay their information back to the scanner.
eDesignSuite. ST proposes a wide range of NFC/RFID evaluation boards and development kits that may be used to perform a comprehensive evaluation of ST25 products and solutions while reducing development time. Our Discovery .
0 · where to get dog microchipped
1 · where are dogs microchips placed
2 · where are dog chips placed
3 · what is a pet microchip
4 · types of microchips for animals
5 · microchip dog identification
6 · dog microchip locations on
7 · chips for dogs identification
As a precautionary measure related to the potential spread of Coronavirus (COVID .
They are radio-frequency identification (RFID) implants that provide permanent ID for your pet. Because they use RFID technology, microchips do not require a power source like a GPS. When a microchip scanner is passed over the pet, .
These microchip implants are called radio frequency identification (RFID) tags. They are tiny, about the size of a large grain of rice, and are passive, which means that they passively store a unique identification number and do not actively transmit any information.They are radio-frequency identification (RFID) implants that provide permanent ID for your pet. Because they use RFID technology, microchips do not require a power source like a GPS. When a microchip scanner is passed over the pet, the microchip gets enough power from the scanner to transmit the microchip’s ID number.
A pet microchip uses radio frequency identification (RFID) technology. RFID, as the name implies, uses radio waves as a medium to transmit information. An RFID tag stores data and, using electromagnetic forces for power, communicates that data to a device that interprets it. A microchip is a radio-frequency identification transponder that carries a unique identification number. It’s roughly the size of a grain of rice. When the microchip is scanned by a vet or.
A: The microchip itself is a passive RFID, which means that it uses radio waves to transmit the information it contains — in this case, your dog’s ID number and the registry’s phone number. These particular chips get powered by the radio wave energy given off by an RFID scanner, which then allows them to relay their information back to the scanner.Universal scanners are becoming more available, and these solve the challenge of detecting different microchip frequencies. Get answers to frequently asked questions about microchips for animals, their benefits, safety, and more. The easiest way to tell if a dog is microchipped is to go to a vet or shelter with an RFID scanner and ask them to scan your dog. You can also try running your hand along your dog’s shoulder blade area to try and feel for a microchip.The chip, about the size of a large grain of rice, uses passive radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology, and is also known as a PIT (passive integrated transponder) tag. Standard pet microchips are typically 11–13 mm long (approximately 1 ⁄ 2 inch) and 2 mm in diameter.
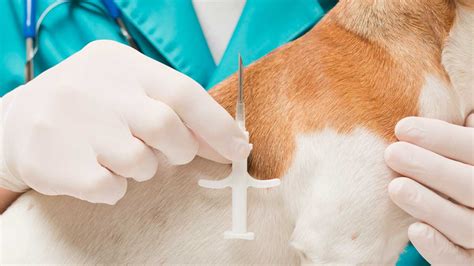
Having your dog microchipped means that a small RFID tag, about the size of a grain of rice, is injected under the skin of your pet. This tag has a unique number that is tied directly to your pet and your personal information, which is registered in a database.
A microchip is a tiny transponder, a radio-frequency identification (RFID) chip. Your veterinarian implants the chip using a needle-like injector, under the dog’s skin in the shoulder area. The process is quick and relatively painless- it feels the same as getting a vaccination.These microchip implants are called radio frequency identification (RFID) tags. They are tiny, about the size of a large grain of rice, and are passive, which means that they passively store a unique identification number and do not actively transmit any information.They are radio-frequency identification (RFID) implants that provide permanent ID for your pet. Because they use RFID technology, microchips do not require a power source like a GPS. When a microchip scanner is passed over the pet, the microchip gets enough power from the scanner to transmit the microchip’s ID number.
A pet microchip uses radio frequency identification (RFID) technology. RFID, as the name implies, uses radio waves as a medium to transmit information. An RFID tag stores data and, using electromagnetic forces for power, communicates that data to a device that interprets it.
A microchip is a radio-frequency identification transponder that carries a unique identification number. It’s roughly the size of a grain of rice. When the microchip is scanned by a vet or.A: The microchip itself is a passive RFID, which means that it uses radio waves to transmit the information it contains — in this case, your dog’s ID number and the registry’s phone number. These particular chips get powered by the radio wave energy given off by an RFID scanner, which then allows them to relay their information back to the scanner.Universal scanners are becoming more available, and these solve the challenge of detecting different microchip frequencies. Get answers to frequently asked questions about microchips for animals, their benefits, safety, and more. The easiest way to tell if a dog is microchipped is to go to a vet or shelter with an RFID scanner and ask them to scan your dog. You can also try running your hand along your dog’s shoulder blade area to try and feel for a microchip.
The chip, about the size of a large grain of rice, uses passive radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology, and is also known as a PIT (passive integrated transponder) tag. Standard pet microchips are typically 11–13 mm long (approximately 1 ⁄ 2 inch) and 2 mm in diameter.Having your dog microchipped means that a small RFID tag, about the size of a grain of rice, is injected under the skin of your pet. This tag has a unique number that is tied directly to your pet and your personal information, which is registered in a database.
how to identify rfid credit cards

where to get dog microchipped
Fans can listen to free, live streaming audio of Auburn Sports Network radio broadcasts of Tiger games and coach's shows. Listen on. Computer; Radio; . TIGER TALK. .
rfid chip in dog|types of microchips for animals