how to encode rfid tags Encoding or programming an RFID tag involves writing a specific set of data or numbers onto an RFID tag’s memory bank. Like we discuss in our article ” Types of Memory in RFID Tags ” there are 4 memory banks on an RFID tag – Reserved memory, EPC memory, TID memory, and User memory, and each has a specific purpose in the function of an RFID tag. Using NFC on Your IPhone. Hold the NFC tag near your iPhone to read it automatically. If you have an older iPhone, open the Control Center and tap the NFC icon. Move the tag over your phone to activate it. The NFC can .
0 · rfid tags encoding formula
1 · rfid tags encoding
2 · rfid tags
3 · rfid tag programming
4 · rfid tag number example
5 · rfid tag codes
6 · rfid card number format
7 · how to program rfid tags
Install the app on an Android phone, and place the back of the android phone over a NFC tag, the app will be launched and displays message on the screen if the NFC tag has .
Some UHF RFID tags are delivered from the manufacturer with a unique, randomized number on the EPC memory bank; however, many shipments are delivered where each tag has the exact same EPC number. RFID is used to uniquely identify items; so, when a tag is assigned to an asset, person, or item, each tag . See moreRegardless if the tag has a unique EPC or not, there are a few reasons to re-encode the EPC number with unique information. Below are a few common scenarios. 1. Encode the EPC number as an item’s serial number or unique product number Working with an . See moreBits are basic units of information and are what is being transmitted between the reader and the tag. Bits are coded in strings of 4, using only ones or zeros. Overall, using strings of bits to communicate data is referred to as Binary Coding. Below is a . See more Encoding or programming an RFID tag involves writing a specific set of data or numbers onto an RFID tag’s memory bank. Like we discuss in our article ” Types of Memory in RFID Tags ” there are 4 memory banks on an RFID tag – Reserved memory, EPC memory, TID memory, and User memory, and each has a specific purpose in the function of an RFID tag.
Selecting the RFID Tag: The first step is to choose the appropriate RFID tag for your application. Consider factors such as tag form factor, read range, memory capacity, and durability.
So, what can you actually encode onto an RFID tag? Usually the information falls into 3 categories: A Random Number. A Custom Number, Identifier, or Coding Scheme. Data and Records. A Random Number. For many applications, users simply encode a Random Number as the tag’s primary ID.Those new to RFID will often elect to encode tags like this: A 12-digit asset ID turned into ASCII characters and stored into the tag. A number starting with 1 or 1,000,000 and incremented for each tag used. An 'SKU' and 'serial' combo stored into the tag ID.
1. Decide which memory bank you will be programming your data to. RFID Tags have 4 main memory banks. Only 2 are re-programmable, the EPC and User memory banks. Learn more about all 4 memory banks by reading our article “ 17 Things You Might Not Know About Gen 2 Memory Banks ". How to Encode an RFID Tag. The RFID technology employs an RFID tag, an RFID reader, and computer software to accurately identify and track objects.
rfid tags encoding formula
How to Encode RFID labels through Zebra Designer V3 and through PRN file. Learn more: https://bit.ly/311zxriDid you know? This is the one costly thing most c.Assuming that you have an RFID reader to read the tags, the data you are going to get is hexadecimal and you need an interpreter to help you determine if the tags are encoded properly. Well, GS1 to the rescue! This session will explain how to encode RFID tags and ensure printing and encoding meet multiple retailers’ requirements.
RFID tags are basically a blank slate of memory, and because many people have no idea what to encode, they consequently devise their own encoding schema—their own data in their own format. This is what we refer to as a proprietary or rogue encoding schema.
Encoding or programming an RFID tag involves writing a specific set of data or numbers onto an RFID tag’s memory bank. Like we discuss in our article ” Types of Memory in RFID Tags ” there are 4 memory banks on an RFID tag – Reserved memory, EPC memory, TID memory, and User memory, and each has a specific purpose in the function of an RFID tag.
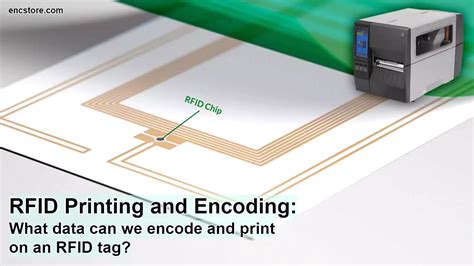
Selecting the RFID Tag: The first step is to choose the appropriate RFID tag for your application. Consider factors such as tag form factor, read range, memory capacity, and durability. So, what can you actually encode onto an RFID tag? Usually the information falls into 3 categories: A Random Number. A Custom Number, Identifier, or Coding Scheme. Data and Records. A Random Number. For many applications, users simply encode a Random Number as the tag’s primary ID.Those new to RFID will often elect to encode tags like this: A 12-digit asset ID turned into ASCII characters and stored into the tag. A number starting with 1 or 1,000,000 and incremented for each tag used. An 'SKU' and 'serial' combo stored into the tag ID. 1. Decide which memory bank you will be programming your data to. RFID Tags have 4 main memory banks. Only 2 are re-programmable, the EPC and User memory banks. Learn more about all 4 memory banks by reading our article “ 17 Things You Might Not Know About Gen 2 Memory Banks ".
How to Encode an RFID Tag. The RFID technology employs an RFID tag, an RFID reader, and computer software to accurately identify and track objects. How to Encode RFID labels through Zebra Designer V3 and through PRN file. Learn more: https://bit.ly/311zxriDid you know? This is the one costly thing most c.Assuming that you have an RFID reader to read the tags, the data you are going to get is hexadecimal and you need an interpreter to help you determine if the tags are encoded properly. Well, GS1 to the rescue! This session will explain how to encode RFID tags and ensure printing and encoding meet multiple retailers’ requirements.
ios nfc tag info

how to use sony nfc tags
Apple has enabled all the iPhones from iPhone 6 to the latest iPhone 12 to work with the NFC tags or cards. The NFC reader on your iPhone can read the information from an . See more
how to encode rfid tags|rfid tags encoding