aloha channel radio frequency vs rain rfid The channel widths vary a lot to accommodate reader (forward link) and tag backscatter (return link) data rates. The RAIN Air Interface has a minimum forward link bit length of 6.25 μs, with 1/6.25 μs = 160 kHz and a maximum frequency for backscatter BLF = 640 kHz.
Shouldnt be anything to worry about. I have a set of NFC cards myself (all the LOZ amiibo before they released the 4 champions) and never had any .
0 · what is rain rfid
1 · rfid vs rain band
2 · rain rfid vs nfc
3 · rain rfid protocol
4 · rain rfid flags
5 · difference between rfid and rain
smartcard-reader. smartcard-reader turns your Android device (running Kitkat or later) into a payment terminal or similar smartcard reader. It uses NFC to interact with a contactless .
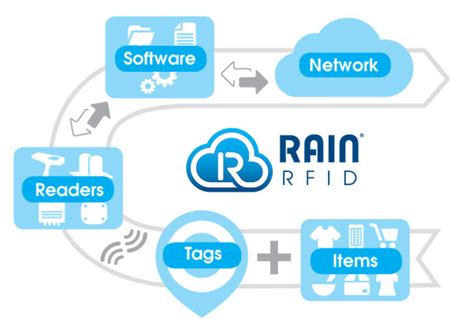
The code for the essential radio frequency regulations settings consists of the 2-letter country code, a digit representing the frequency range and a letter to distinguish the available options. For countries that are not listed there is no RAIN RFID recommendation available yet. Country . Two of the most popular forms of RFID are NFC and RAIN RFID. At 13.56 .The code for the essential radio frequency regulations settings consists of the 2-letter country code, a digit representing the frequency range and a letter to distinguish the available options. For countries that are not listed there is no RAIN RFID recommendation available yet. Country codes may be added in a future edition of this document.Two of the most popular forms of RFID are NFC and RAIN RFID. At 13.56 megahertz, NFC is a high-frequency RFID, while RAIN (whose acronym — a nod to its reach into the cloud — derives from “RAdio frequency IdentificatioN”) is an ultrahigh-frequency RFID .
RAIN is a branded term for Passive Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID technology. There are five common frequency ranges that RFID technology uses: Low-Frequency (125-134 KHz), High-Frequency and NFC (13.56 MHz), Active UHF (433 MHz), Passive UHF (860-960 MHz), and Microwave (2.45-5.8 GHz).The channel widths vary a lot to accommodate reader (forward link) and tag backscatter (return link) data rates. The RAIN Air Interface has a minimum forward link bit length of 6.25 μs, with 1/6.25 μs = 160 kHz and a maximum frequency for backscatter BLF = 640 kHz.
Understanding the frequencies with its specific characteristics at which RFID systems operate will help you to determine which automatic vehicle identification solution may be suitable for your application. UHF band spans a spectrum of frequencies from 300 MHz to 3 GHz, while RAIN RFID devices function within this UHF band (860-960 MHz) and comply with a particular standard and protocol. RAIN RFID systems, operating within the UHF frequency range, are synonymous with UHF RFID. By utilizing radio frequency signals, Rain RFID enables the identification and tracking of objects without the need for physical contact. It involves the use of tags, which are small electronic devices, and readers, which are devices capable of . RFID is a generic term that encompasses different operating frequencies and standards. UHF, which stands for “ultra-high frequency,” is a frequency band that covers the range from 300 MHz to 3 GHz. RAIN RFID devices operate within the UHF band (between 860 to 960 MHz) and align with a specific standard and protocol.
In this paper, we propose a dynamic slotted-ALOHA-based medium-access control approach for FANETs. Our dynamic random access approach is composed of two substan-tial steps: one of them is the estimating UAV density, and the second step is the adaptation of the channel access probabilities of UAVs based on the estimated UAV density. We claim
what is rain rfid
2.4 Essential radio frequency regulations settings. Table 1 defines recommended RAIN RFID settings for UHF RFID regulations in various regions and countries, as developed by the RAIN Alliance. The Table 1 headers are described in detail in Table 2. The intention of RAIN is to keep the number of different codes as small as possible.The code for the essential radio frequency regulations settings consists of the 2-letter country code, a digit representing the frequency range and a letter to distinguish the available options. For countries that are not listed there is no RAIN RFID recommendation available yet. Country codes may be added in a future edition of this document.Two of the most popular forms of RFID are NFC and RAIN RFID. At 13.56 megahertz, NFC is a high-frequency RFID, while RAIN (whose acronym — a nod to its reach into the cloud — derives from “RAdio frequency IdentificatioN”) is an ultrahigh-frequency RFID . RAIN is a branded term for Passive Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID technology. There are five common frequency ranges that RFID technology uses: Low-Frequency (125-134 KHz), High-Frequency and NFC (13.56 MHz), Active UHF (433 MHz), Passive UHF (860-960 MHz), and Microwave (2.45-5.8 GHz).
The channel widths vary a lot to accommodate reader (forward link) and tag backscatter (return link) data rates. The RAIN Air Interface has a minimum forward link bit length of 6.25 μs, with 1/6.25 μs = 160 kHz and a maximum frequency for backscatter BLF = 640 kHz.
Understanding the frequencies with its specific characteristics at which RFID systems operate will help you to determine which automatic vehicle identification solution may be suitable for your application.
UHF band spans a spectrum of frequencies from 300 MHz to 3 GHz, while RAIN RFID devices function within this UHF band (860-960 MHz) and comply with a particular standard and protocol. RAIN RFID systems, operating within the UHF frequency range, are synonymous with UHF RFID.
rfid vs rain band
rain rfid vs nfc
rain rfid protocol
By utilizing radio frequency signals, Rain RFID enables the identification and tracking of objects without the need for physical contact. It involves the use of tags, which are small electronic devices, and readers, which are devices capable of . RFID is a generic term that encompasses different operating frequencies and standards. UHF, which stands for “ultra-high frequency,” is a frequency band that covers the range from 300 MHz to 3 GHz. RAIN RFID devices operate within the UHF band (between 860 to 960 MHz) and align with a specific standard and protocol.
In this paper, we propose a dynamic slotted-ALOHA-based medium-access control approach for FANETs. Our dynamic random access approach is composed of two substan-tial steps: one of them is the estimating UAV density, and the second step is the adaptation of the channel access probabilities of UAVs based on the estimated UAV density. We claim
flexsmart prox and mifare card
rfidiot acr122u
Here is how the “Handheld RFID Writer” (that you can easily purchase for less than $10) works: Turn on the device. Hold a compatible EM4100 card or fob to the side facing the hand grip and click the ‘Read’ button. The .
aloha channel radio frequency vs rain rfid|rain rfid flags