reader and tag collisions rfid The tag-to-tag collision problem seriously affects the identification performance of the RFID system, which causes the reader to be unable to accurately identify any tag within the specific time. The mainstream anticollision algorithms are limited by the performance bottleneck under the standard framework.
NFC, or near-field communication, is a short-range wireless technology that allows your phone to act as a transit pass or credit card, quickly transfer data, or instantly pair with Bluetooth .About the YubiKey and smart card capabilities. YubiKey 5 NFC, YubiKey 5 Nano, YubiKey 5C, and YubiKey 5C Nano provide Smart Card functionality based on the Personal Identity Verification (PIV) interface specified in NIST SP 800-73, “Cryptographic Algorithms and Key Sizes for .
0 · rfid anti collision algorithm
1 · mdpi anti collision tags
2 · anti collision tags rfid
3 · anti collision tags
4 · anti collision rfid
If you don't have NFC tools to format blank cards, use the free iphone App NFC TagWriter first to format, then either you clone an existing card like the welcome one, and change the link, or you create a custom content and then get it .
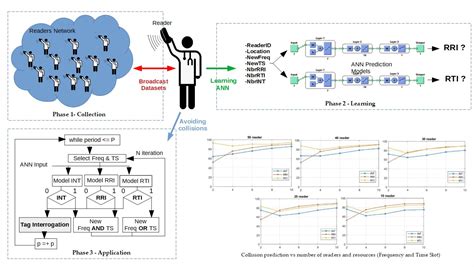
To minimize tag collisions, RFID readers must use an anti-collision protocol. Different types of anti-collision protocols have been proposed in the literature in order to solve this problem. This .To address this problem, this article proposes a time-efficient protocol stack that is tailored to the tag identification in a multireader RFID system, which consists of two protocols: one is for . The tag-to-tag collision problem seriously affects the identification performance of the RFID system, which causes the reader to be unable to accurately identify any tag within .To minimize tag collisions, RFID readers must use an anti-collision protocol. Different types of anti-collision protocols have been proposed in the literature in order to solve this problem. This paper provides an update including some of the most relevant anti-collision protocols.
rfid anti collision algorithm
mdpi anti collision tags
To address this problem, this article proposes a time-efficient protocol stack that is tailored to the tag identification in a multireader RFID system, which consists of two protocols: one is for eliminating reader collision (RCE) and the other is for avoiding tag-to-tag collision (TCE). The tag-to-tag collision problem seriously affects the identification performance of the RFID system, which causes the reader to be unable to accurately identify any tag within the specific time. The mainstream anticollision algorithms are limited by the performance bottleneck under the standard framework.
In short, the RFID tag anti-collision algorithm based on machine learning can greatly improve the accuracy and efficiency of tag identification, and reduce interference and repeated reading between tags, especially in large-scale RFID applications.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) tag anticollision algorithm is a key technology that affects the performance of RFID systems. In dynamic arrival scenarios, when the tags arrive the reader’s interrogation zone, they cannot participate in the ongoing identification immediately, resulting in longer waiting time and tag miss.
In RFID systems, reader interference can be divided into two categories: reader-to-tag and reader-to-reader collision. (a) In a reader-to-tag collision, as shown in Figure 2a, two readers want to identify a tag that is within their common reading range at the same time [15].RFID reader collision happens when two different readers are placed within the RFID range; thus, the collision occurs. In simpler words, it is a phenomenon where two readers can read each other, interfering with the tag reading.Tag collision is the event that the interrogator (reader) cannot identify the data of tag when more than one tag occupies the same communication channel simultaneously. The reason is that whenever two or more users are transmitting on the shared channel simultaneously, a collision occurs and the data cannot be received correctly.
The second type, reader and reader collision occurs when a tag is supposed to come under reader X enters the proximity of reader . ALOHA algorithm and binary search algorithms can be classified as the two of major algorithms which are specifically used to avoid the RFID tag collisions.
Tag collision happens when two or more tags reflects-back their individual identification radio signals to the reader at the same time thus confusing the reader identification process. Different algorithmic solutions on tag collision are available.To minimize tag collisions, RFID readers must use an anti-collision protocol. Different types of anti-collision protocols have been proposed in the literature in order to solve this problem. This paper provides an update including some of the most relevant anti-collision protocols.To address this problem, this article proposes a time-efficient protocol stack that is tailored to the tag identification in a multireader RFID system, which consists of two protocols: one is for eliminating reader collision (RCE) and the other is for avoiding tag-to-tag collision (TCE). The tag-to-tag collision problem seriously affects the identification performance of the RFID system, which causes the reader to be unable to accurately identify any tag within the specific time. The mainstream anticollision algorithms are limited by the performance bottleneck under the standard framework.
In short, the RFID tag anti-collision algorithm based on machine learning can greatly improve the accuracy and efficiency of tag identification, and reduce interference and repeated reading between tags, especially in large-scale RFID applications. Radio-frequency identification (RFID) tag anticollision algorithm is a key technology that affects the performance of RFID systems. In dynamic arrival scenarios, when the tags arrive the reader’s interrogation zone, they cannot participate in the ongoing identification immediately, resulting in longer waiting time and tag miss. In RFID systems, reader interference can be divided into two categories: reader-to-tag and reader-to-reader collision. (a) In a reader-to-tag collision, as shown in Figure 2a, two readers want to identify a tag that is within their common reading range at the same time [15].
anti collision tags rfid
RFID reader collision happens when two different readers are placed within the RFID range; thus, the collision occurs. In simpler words, it is a phenomenon where two readers can read each other, interfering with the tag reading.
Tag collision is the event that the interrogator (reader) cannot identify the data of tag when more than one tag occupies the same communication channel simultaneously. The reason is that whenever two or more users are transmitting on the shared channel simultaneously, a collision occurs and the data cannot be received correctly. The second type, reader and reader collision occurs when a tag is supposed to come under reader X enters the proximity of reader . ALOHA algorithm and binary search algorithms can be classified as the two of major algorithms which are specifically used to avoid the RFID tag collisions.
Manage your adult Oyster and contactless cards on the move with the app. • Top up pay as you go credit. • Buy adult rate 7 Day, Monthly and Annual Travelcards, and Bus & Tram Passes. • View your Oyster card and contactless journey .
reader and tag collisions rfid|rfid anti collision algorithm