identify lf or hf rfid card Learn how to identify different RFID card type, including LF, HF, and UHF, to ensure . NFC basics. This document describes the basic NFC tasks you perform in Android. It explains how to send and receive NFC data in the form of NDEF messages and describes the Android framework APIs that support .
0 · rfid frequency requirements
1 · rfid frequency examples
2 · rfid frequency chart
3 · rfid card type identification
4 · rfid band frequency
5 · rfid application frequency
6 · how to identify rfid card
7 · choosing a rfid frequency
About. NFC NDEF Reader and Writer for Android studio - Kotlin. kotlin kotlin .
fanvill i30 type of access control cards
rfid frequency requirements
Understanding the differences in RFID frequencies is particularly important when choosing the right RFID solution. This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), HF (high frequency), and UHF (ultra-high .Learn how to identify different RFID card type, including LF, HF, and UHF, to ensure .Understanding the differences in RFID frequencies is particularly important when choosing the right RFID solution. This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), .
rfid frequency examples
Learn how to identify different RFID card type, including LF, HF, and UHF, to ensure compatibility and efficiency in your RFID system.
LF RFID is ideal for environments where the tags are close to the reader and there may be metal or liquid interference. It’s also better suited for use cases where a slower data transfer rate is acceptable. The most common applications of LF RFID include: Animal tracking: Used in tagging pets, livestock, and wildlife.Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.
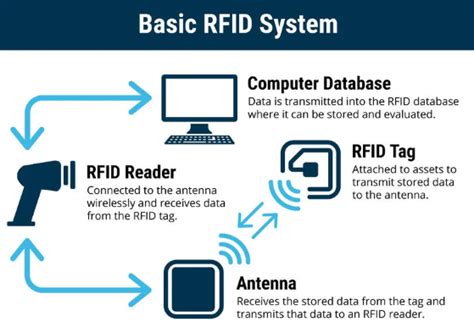
There are three main types of RFID cards: low-frequency (LF), high-frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF). Here are some ways to identify them: • Look for physical markings or logos. Some RFID cards have visible markings or logos that indicate the card manufacturer, card format, frequency, or other information. Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware.
In this article, we will explore the different RFID frequencies, namely Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra High Frequency (UHF), and discuss various methods to find the frequency of an RFID system.How to Select a Correct Tag – Frequency. RFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID systems. • Low frequency (LF) • High frequency (HF) • Ultra high frequency (UHF) • Microwave frequency (microwave)This article provides a guide on RFID Frequency Ranges: LF, HF, UHF, and Microwave. We will explore how these frequencies enable a variety of applications, providing clarity to make informed decisions in the exciting world of radio frequency identification.Of the eight frequencies on the radio wave band, there are three that are typically used for RFID applications: Low frequency (LF) High frequency (HF) Ultra-high frequency (UHF) Low Frequency About. The Low Frequency, or LF band, is between 30 kHz and 300 kHz with long wavelengths of around 2,400 meters.
Understanding the differences in RFID frequencies is particularly important when choosing the right RFID solution. This article will analyze in detail the characteristics and application differences of the three RFID frequencies: LF (low frequency), .Learn how to identify different RFID card type, including LF, HF, and UHF, to ensure compatibility and efficiency in your RFID system. LF RFID is ideal for environments where the tags are close to the reader and there may be metal or liquid interference. It’s also better suited for use cases where a slower data transfer rate is acceptable. The most common applications of LF RFID include: Animal tracking: Used in tagging pets, livestock, and wildlife.Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.
There are three main types of RFID cards: low-frequency (LF), high-frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF). Here are some ways to identify them: • Look for physical markings or logos. Some RFID cards have visible markings or logos that indicate the card manufacturer, card format, frequency, or other information. Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware. In this article, we will explore the different RFID frequencies, namely Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra High Frequency (UHF), and discuss various methods to find the frequency of an RFID system.How to Select a Correct Tag – Frequency. RFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID systems. • Low frequency (LF) • High frequency (HF) • Ultra high frequency (UHF) • Microwave frequency (microwave)
This article provides a guide on RFID Frequency Ranges: LF, HF, UHF, and Microwave. We will explore how these frequencies enable a variety of applications, providing clarity to make informed decisions in the exciting world of radio frequency identification.
rfid frequency chart
rfid card type identification
how to access graphics card control panel xps 13
miwa access control card
$19.48
identify lf or hf rfid card|rfid card type identification