rfid tag power consumption The battery capacity of an active RFID tag is determined by factors like the power consumption of the tag’s components, the desired operational lifespan, and the frequency and duration of signal transmission. $19.48
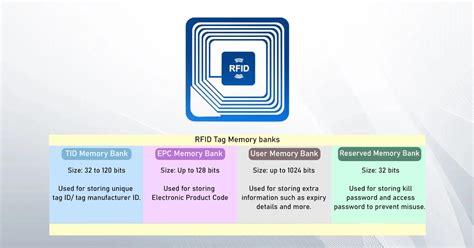
0 · storage capacity of rfid tags
1 · rfid memory capacity
2 · rfid medical records
3 · rfid medical record storage
4 · rfid logistics data storage
5 · rfid data storage capacity
6 · how much rfid holds
7 · data storage rfid
Nintendo's amiibo success has for a long time left original 3DS owners out in the cold. Not any more though! Nintendo has released the amiibo NFC adapter tha.
The battery capacity of an active RFID tag is determined by factors like the power consumption of the tag’s components, the desired operational lifespan, and the frequency and duration of signal transmission. The battery capacity of an active RFID tag is determined by factors like the power consumption of the tag’s components, the desired operational lifespan, and the frequency and duration of signal transmission. How much electricity (voltage and current) does a passive RFID transponder generate upon receiving a radio signal, and on which factors are a tag’s electric power dependent? 1. Tag Activation: When an RFID tag enters the range of an RFID reader, the reader emits radio waves or electromagnetic fields. These waves provide the necessary energy to the passive RFID tag, allowing it to power up and respond.
Here are several ways to reduce power consumption for the RFID: Power-saving modes. Battery-operated RFID interrogators have a set of internal power-saving modes. These different modes can offer different levels of power savings. Passive RFID systems use tags with no internal power source and instead are powered by the electromagnetic energy transmitted from an RFID reader. Passive RFID tags are used for applications such as access control, file tracking, race timing, supply chain management, smart labels, and more.Tag operational power requirements can go as low as 200 microwatts absorbed from the RF field. Since there is not enough field power to operate a traditional RF transmission, passive RFID tags communicate back to the reader with a technique called ‘backscatter’. In this paper, we show that negative differential resistance devices, such as tunnel diodes, exhibit 27 dB more gain and 10 dB lower power consumption than state-of-the-art reflection amplifiers.
The whole RFID tag chip achieved an ultra-low power of <19.5 µW in a considerable small chip area of 4.7 mm 2. Power consumption and operating time are major factors to affect the battery life of an RFID reader. We tested and evaluated different power saving options. In this article, a novel ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) radio frequency identification (RFID) passive tag with a current sensor is presented. The device can be used to detect electrical current flowing through the power cord of the surveyed equipment, allowing for its switched on state to be established and, for instance, its energy consumption to . The battery capacity of an active RFID tag is determined by factors like the power consumption of the tag’s components, the desired operational lifespan, and the frequency and duration of signal transmission.
How much electricity (voltage and current) does a passive RFID transponder generate upon receiving a radio signal, and on which factors are a tag’s electric power dependent? 1. Tag Activation: When an RFID tag enters the range of an RFID reader, the reader emits radio waves or electromagnetic fields. These waves provide the necessary energy to the passive RFID tag, allowing it to power up and respond.Here are several ways to reduce power consumption for the RFID: Power-saving modes. Battery-operated RFID interrogators have a set of internal power-saving modes. These different modes can offer different levels of power savings.
Passive RFID systems use tags with no internal power source and instead are powered by the electromagnetic energy transmitted from an RFID reader. Passive RFID tags are used for applications such as access control, file tracking, race timing, supply chain management, smart labels, and more.
storage capacity of rfid tags
Tag operational power requirements can go as low as 200 microwatts absorbed from the RF field. Since there is not enough field power to operate a traditional RF transmission, passive RFID tags communicate back to the reader with a technique called ‘backscatter’. In this paper, we show that negative differential resistance devices, such as tunnel diodes, exhibit 27 dB more gain and 10 dB lower power consumption than state-of-the-art reflection amplifiers. The whole RFID tag chip achieved an ultra-low power of <19.5 µW in a considerable small chip area of 4.7 mm 2.
Power consumption and operating time are major factors to affect the battery life of an RFID reader. We tested and evaluated different power saving options.
rfid memory capacity
rfid medical records
rfid medical record storage
NFC stands for Near-field communication. See more
rfid tag power consumption|rfid memory capacity